It’s almost the most wonderful time of the year! And we know it’s also retail’s busiest, so we’re here to help you get in the holiday spirit and also make sure you get the most magic (and ROI) out of your personalization platform.
Last night RichRelevance and Shop Direct were crowned as leaders at The Retail Systems Awards at the Millennium Hotel, in Mayfair, London.
About 15 years ago, I was working for a little marketing agency creating banners and ads for websites. On average, a client had around 10-12 such banners. The rule of thumb was that if a banner was relevant to about 80% of the audience, we’d build it. A “20% off everything“ for everyone campaign would surely meet this criteria. Building a banner targeted to a handful of shoppers was simply not done, it was unthinkable.
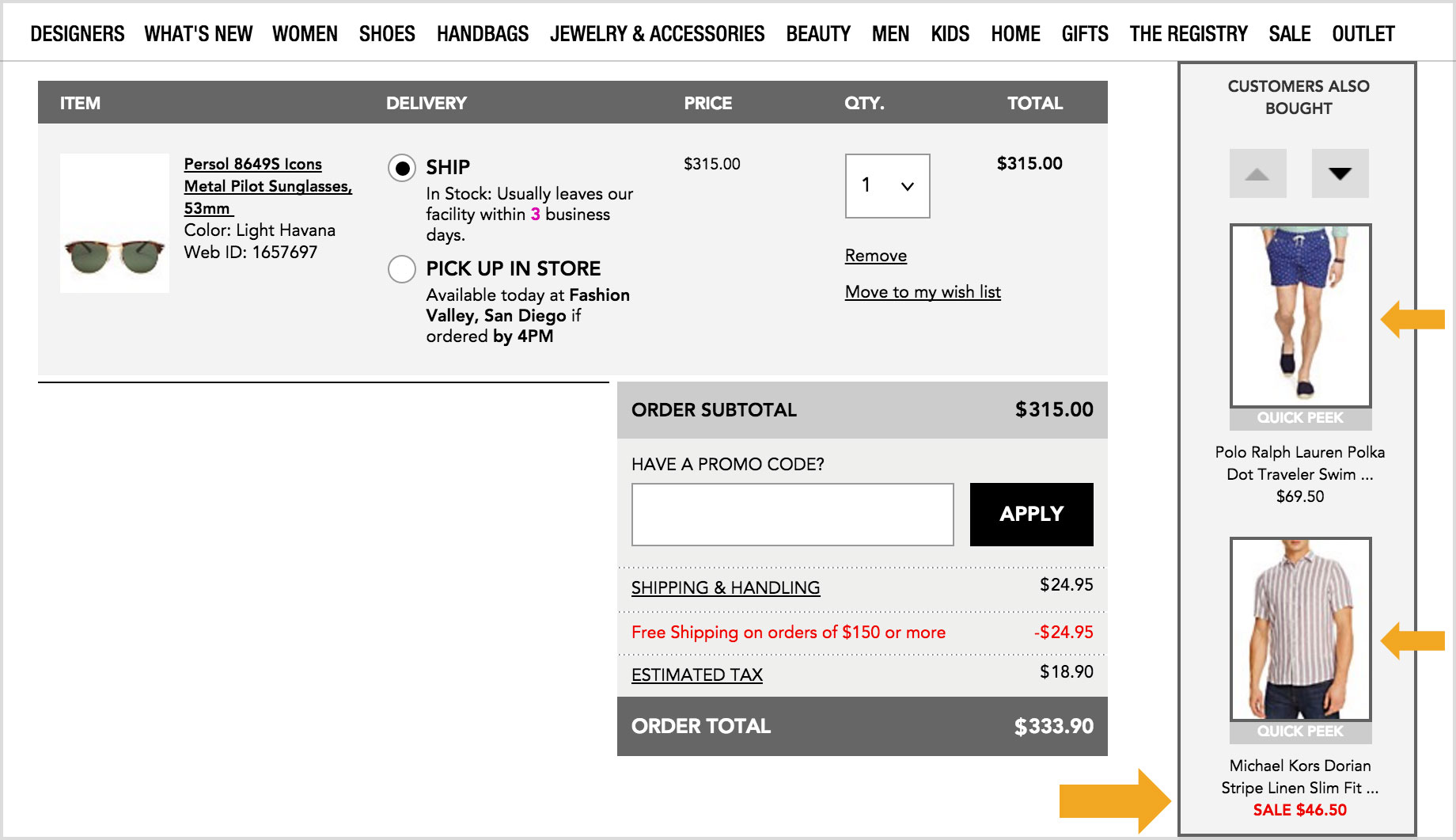
You spend a lot of time optimizing your website to streamline the shopper’s path through the retail funnel—making sure they see value at each point along the way. Once you navigate the shopper to the right product, it’s important that you take the necessary steps to seal the deal, and get the shopper across the finish line.
The cart page is a pivotal area for securing that conversion. When done well, you’ll get the sale, and then potentially entice the shopper to buy more items. When done poorly, you’ll disrupt conversion by distracting the shopper from the transaction you’ve fought so hard to get.
And so we ask: How smart is your cart?
At RichRelevance, we’re sensitive to the cart page experience, and work closely with our retail partners to implement solutions deep in the funnel that will grow cart values without compromising conversion. Here are three things you can do with product recommendations to substantially enhance your cart page experience:
1. Get out of the way
Securing conversion is our primary objective on the cart page. If we can get the shopper to buy more stuff and grow the order value, that’s phenomenal! But, it shouldn’t compromise completing the sale. The location of recommendations must reflect this prioritization and not interfere with the shopper consuming information critical to the buying decision.
As such, recommendations must be on the periphery of core content such as the cart summary, checkout call-to-action, promotional code inputs, and other key messaging and functionality. This usually means slotting a vertical placement in the right margin or a horizontal placement underneath the main content area. Otherwise, if more prominently placed, you’re baiting customers to continue shopping, which can be extremely disruptive to conversion.
2. Recommend complementary, non-competitive products
When you finally get the shopper to the cart page, it’s critical not to challenge their decision to buy. If they add a TV to their shopping bag, they’ve demonstrated a degree of commitment that we shouldn’t impede by recommending another TV upon landing on the cart page. Instead of being helpful, that would be frustrating to the shopper, and elicitreconsideration at a point when a shopper should be firm about their core purchase
On the cart page, it’s imperative to use cross-sell recommendations that display products most often purchased with the seed item. However, since these kinds of recommendations rely on purchase behavior at the individual product level, something that happens much less frequently than browse activity, , it can be challenging for behavioral recommendations systems to always deliver intuitive cross-sell recommendations across a retailer’s entire catalog.
As an example, if a specific TV model has only been purchased 50 times in recent history, that’s probably not enough transactions to reliably identify four or five logical products that are commonly purchased with it. You can overcome this dilemma, in 2 ways:
I. Incorporate point-of-sale (POS) data in recommendations. If you have a brick-and-mortar presence, you probably have more offline POS transactions than online sales. Incorporating those in your online recommendations will provide a wealth of data from which to identify logical product associations.
II. Employ rule-based recommendations. Create a set of advanced merchandising rules that governs what is recommended in cross-sell situations. For each category of products, define what categories you want represented in each recommendation slot—and then let the engine source products based on whatever brand, attribute or compatibility-matching requirements you might have configured.
Ok, so now you have well-placement recommendations and you’ve optimized your cross-sell assortment across your entire catalog. What’s left?
3. Optimize your recommendations layout
Once you’ve gotten the shopper to the cart page, create inertia that pushes them through the checkout process rather than casting them out to higher parts of the funnel. You can do this by presenting a recommendation layout that facilitates exploring a product and adding it to cart without leaving the current page. Implement ‘quick view’ functionality on recommendations that allows a shopper to access product information, configuration options (e.g., size/color), and add-to-cart capabilities with a single click. Without this functionality, you’re forcing shoppers to leave the cart page to explore recommended products, and they may never come back.
Your cart page is sacred as it’s the gateway to more cash in your coffers. It’s imperative that the page experience drive shoppers to transact rather than pull them into a dangerous loop of product reconsideration. These are merely a small sample of tactics RichRelevance has deployed and validated using rigorous A/B and multivariate testing. We strongly encourage you to consider these optimizations for your retail site. They’ll make your cart smarter, protect your conversions, and grow your order values.
Last week over 200 in-store innovators from 120 enterprise retailers, gathered at Future Stores in the Victoria Park Plaza in London. The event is a ‘one-stop-shop’ for retailers seeking practical solutions to accelerate their in-store transformation projects from concept to reality.
There were many interesting topics covered from in-store design to leveraging data from digital channels to adapt in-store experiences. The common thread throughout all the conversations, presentations and debate – was putting the customer at the heart of all strategies and initiatives; from driving customer engagement to improving their experience and making their shopping journey as easy as possible.
One of the most interesting debates was about the use of technology in-store. It was abundantly clear retailers are either embracing it or running in the opposite direction. There are perfectly legitimate reasons as to why a retailer is on one side of the fence or the other.
Where a retailer has a high turnover of sales staff with busy stores and peaks at checkout tills, utilizing technology on the shop floor can certainly enhance the customer’s experience. In this scenario, arming sales assistants with access to stock levels, personalized recommendations and complementary products plus the ability to take payments on the shop floor, improves the experience for customers, saving them time and results in more sales and less returns.
However, if a retailer has highly trained, loyal sales assistants who are knowledgeable and enthusiastic product advocates, who act as personal advisors to their shoppers, supporting technology to help the sales process is arguably reduced.
Regardless of the environment or scenario, it’s agreed that technologies introduced to the in-store experience should be complementary to the shopping journey – not a distraction for associates and shoppers alike.
Ultimately, it will be the customer who decides. As our ‘Creepy/Cool’ survey from 2015 revealed, shoppers also have different attitudes towards technology in-store. Where some shoppers embrace features such as facial recognition and interactive mirrors making product suggestions in changing rooms as cool, others are turned off at the mere thought. Therefore, the type of customer a retailer has will influence their use of technology in-store. That said, attitudes can and often do change over time, and I’m certainly looking forward to the latest ‘Creepy/Cool’ survey results, which are out in the next few weeks.
Overall, we thoroughly enjoyed the debate at Future Stores, and we’re looking forward to their next event in Seattle in just a few weeks time.
The usage of proximity-based beacons seems to have floundered since they were introduced in 2013. After reading this very interesting article about the Regent Street App, it is obvious why. Unfortunately, many retailers, and even some tech companies, think of beacons as just a tool to trigger push notifications. From this perspective it is understandable why many would assume that beacons do more damage than good; using beacons to trigger endless location-based notifications would equate to a type of spam, resulting in an irritated customer.
In truth, beacons are way more than a vehicle for push notifications if you understand how to use them correctly. Here’s why:
Beacons are dumb, technically speaking. The only thing they do is broadcast a specific string. For example, the beacon might broadcast its name and location, such as number 123. That’s all. It’s up to the application and infrastructure behind the beacon to make any sense of it. Essentially, beacons are passive and can be used to deliver whatever string it is programmed to.
Ok, so now you’re thinking: what does that mean and how should retailers use them?
Here’s some food for beacon-thought. Please note that this is by no means a comprehensive list of beacon applications. However, if you are using a sophisticated personalization platform, these should all be relatively simple to deploy:
Store Identifier
Suppose you only have one beacon in a chain of stores and an app that can pick up the signal. What can you do with it? First you can provide the beacon with the name of your store, for example: “New York, 5th Avenue”. Once the shopper enters the store and the app picks up the beacon, you can write this event in a centralized user profile so that you know that specific shopper entered that specific store. Based on this information, you can then determine the frequency the shopper comes into your store(s). If you find the shopper frequents one store more often than others, you can determine this is his/her preferred store. Once you know his preferred store, you can send him promotions and offers from that specific store and always make sure you show the inventory of products at that location.
Department Locator
If you place beacons around the store in departments such as shoes, coats and perfumes. When the shopper opens up the app in the store, the app picks up the the signal of the beacon; the beacon will know where the shopper is specifically in the store and will display the appropriate and relevant content. When the app is opened in the shoes department, it will show content for shoes. When it’s in the perfumes section, it will show content for perfumes – you get the idea. The information about which department has been visited can be stored in the centralized user profile, so that when the user logs onto his/her mobile device or home computer, he or she is greeted with relevant content.
Re-Engagement Trigger
Given that the beacon has learned and retained all of this information in the centralized user profile, a retailer can leverage these learning and behaviors to intelligently re-engage and welcome the shopper when he/she returns to the store. With every trigger, previous behaviors can be recalled to facilitate a curated conversation and a customer experience that learns and adapts with the customer.
Connecting the Dots
Another valuable type of information is offline purchase data, which can be ingested into the centralized user profile through the means of a loyalty card program or e-receipts. When you find that a shopper visited the fragrance department and viewed various fragrances on his/her mobile while navigating the store, but ultimately didn’t purchase a fragrance, you can re-engage with him/her by triggering personalized email with content from this section and products he/she looked at.
The retail landscape demands that the customer experience becomes simpler, more intuitive and more personal than ever before. And today, every shopper navigates the aisles and departments of his or her preferred retailers with mobile devices in hand; beacons help connect the customer journey, bringing the digital and physical worlds together for a harmonious experience.